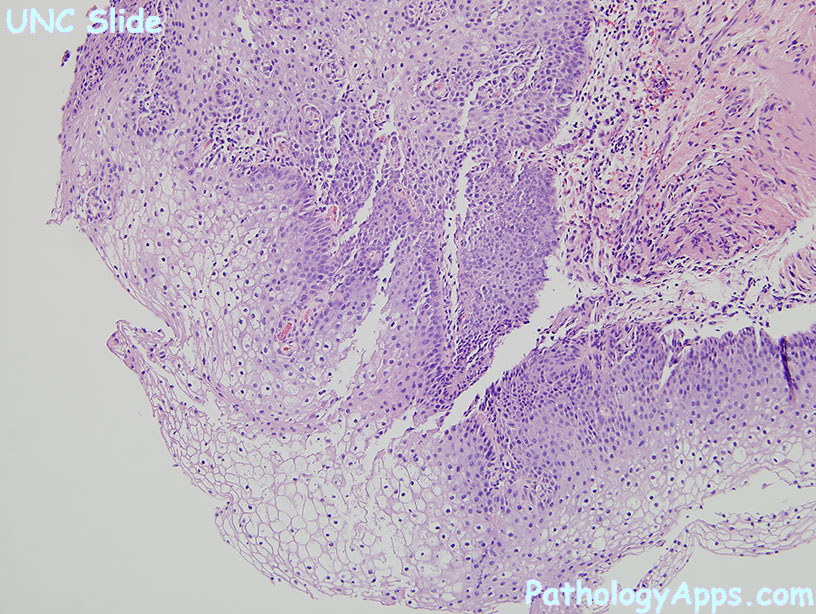
Squamous metaplasia is a benign non-cancerous change (metaplasia) of surfacing lining cells (epithelium) to a squamous morphology.
Location
Common sites for squamous metaplasia include the bladder and cervix. Smokers often exhibit squamous metaplasia in the linings of their airways. These changes don't signify a specific disease, but rather usually represent the body's response to stress or irritation. Vitamin A deficiency or overdose can also lead to squamous metaplasia.
Uterine cervix
In regard to the cervix, squamous metaplasia can sometimes be found in the endocervix, as it is composed of simple columnar epithelium, whereas the ectocervix is composed of stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium.
Significance
Squamous metaplasia may be seen in the context of benign lesions (e.g., atypical polypoid adenomyoma), chronic irritation, or cancer (e.g., endometrioid endometrial carcinoma), as well as pleomorphic adenoma.
See also
- Metaplasia
- Dysplasia
- Barrett esophagus - a columnar cell metaplasia of squamous epithelium
- Subareolar abscess
References